Back on Track: CARB Delivers Long-awaited CCA Workshop with No Major Surprises
4 Min. Read Time
CARB, the California Cap-and-Invest market regulator, delivered pragmatic policy updates with no major surprises during its public workshop on Wednesday, October 29. The updates on potential amendments to the program, framed in the context of the latest legislation AB1207 and SB 840, focused on the cap trajectory scenarios, inclusion of offsets under the cap, potential carbon leakage assessment, and free allocation adjustments. This year, the extension legislation (AB 1207) became the top priority, with the rulemaking process effectively sidelined until its passage; as a result, reform progress was delayed, with the last public workshop held back in July of last year.
Dec25 CCA futures dipped slightly intraday before recovering to close up 1.2% at $32.42 on the day of the workshop. CARB's preference for the baseline 40% target (lower than 48% scenarios previously floated) was largely anticipated. The clarity and market confidence that comes with the extension through 2045 and the allowance removals from the cap (including offset reductions) provide strong structural support for prices over the long term. The full slide deck used in the workshop can be found here.

Key Takeaways:
- CARB leaning toward cap trajectory of 118Mt allowance removal from 2027-2030 budgets to align with a 40% emissions reduction target by 2030 and confirmed no removals from reserves (tier levels & ceiling).
- Rulemaking timeline: Initial Statement of Reasons (ISOR) that outlines specifics on the market reform is expected by year-end, with final vote in Q2 2026
- Adressing the offset-use variability over multi-year compliance cycles and its impact on auction supply now that its included under the cap
CARB started the discussion with an overview of past updates to the Cap-and-Invest program (summarized below), which was followed by a deep dive into the main policy topics.

Allowance budget scenarios update
- Minimum of 118 million allowances would be removed over 2027-2030 and a smooth cap decline in subsequent years
- CARB appears to be maintaining the statutory 40% emissions reduction target (baseline) rather than the 2022 Scoping Plan 48% reduction by 2030, largely in response to addressing the hot topic of affordability and assumptions of reduced federal assistance for California climate objectives.
- Announced a potential 2045 annual allowance endpoint of 30.3 million in 2045 to align with the 85% reduction target and carbon neutrality targets.
Address inclusion and impact of offsets under the cap
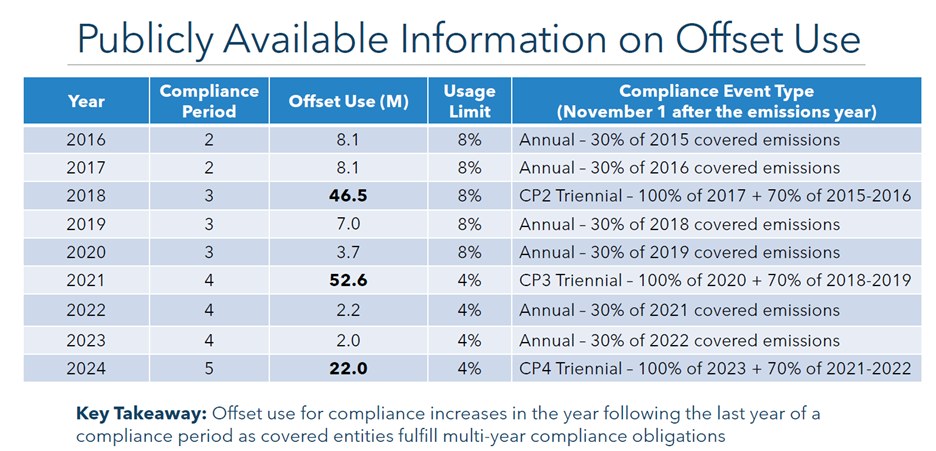
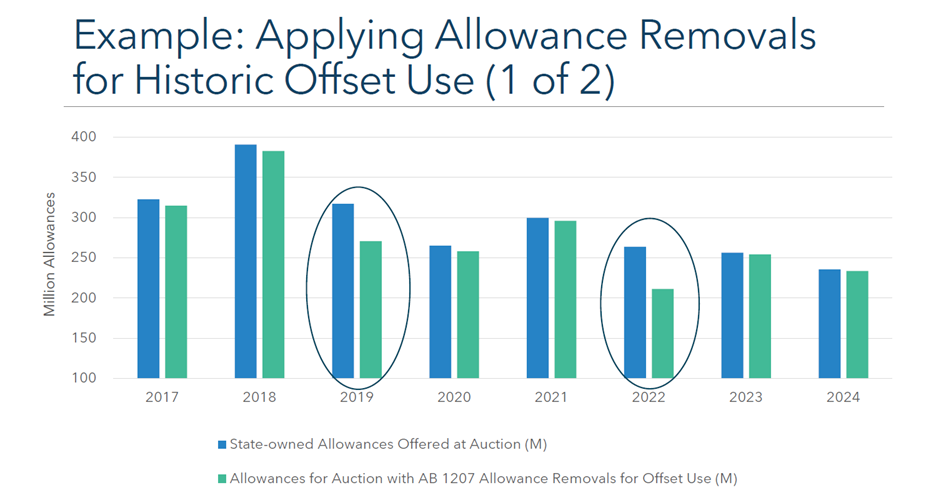
- Address impact of “offsets under the cap,” i.e., the use of offsets (max of 6% for compliance obligations) will now be deducted the following year’s annual allowance budget.
- Historically, the number of offsets surrendered spikes at end of the (3-year) compliance cycle, meaning there is less supply and auction proceeds are reduced in the year after a full compliance period compliance event.
- Technically, there is a 2-year lag between offset use and reduction in cap: e.g., offsets used for compliance in 2026 are surrendered in Nov 2027. The allowance budget from which equivalent allowances are retired corresponds to the year after the surrender year, so allowances are retired from the 2028 budget.
- CARB Public Input: how to address the offset use variability over multi-year compliance cycles and its impact on auction supply.
Industrial allowance allocation methodology to cost-effectively minimize emissions leakage risk
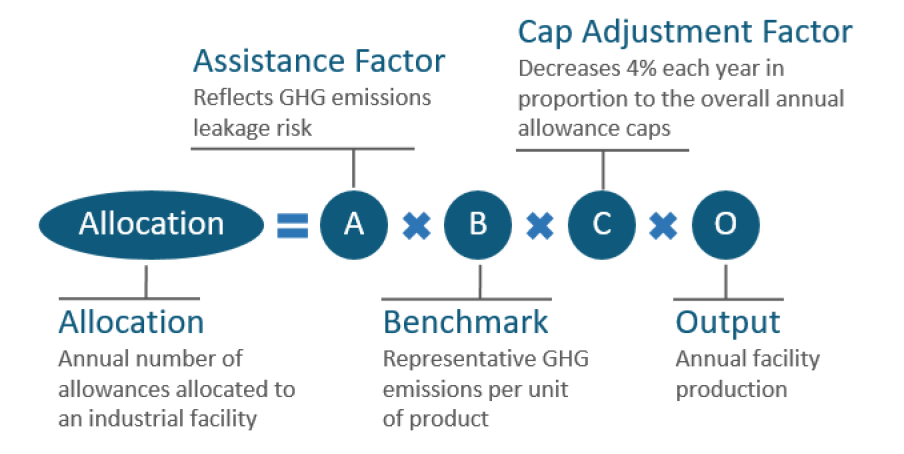
- Background: Hard to abate industrial sectors receive allowances at no cost (free allowances) to help prevent carbon leakage, where the allocations are calculated using an output-based method (see equation below).
- CARB may adjust the Cap Adjustment Factor (CAF) for free allocations of CCAs to industrial sectors. For most facilities, allocation declines annually per the CAF, which declines in proportion to the overall annual budgets.
- CARB emissions leakage study (2011-2021 observed period) found no evidence that the Cap-and-Invest program caused leakage in the electricity sector (also referred to as “Resource Shuffling” – i.e., companies leave the state to avoid CCA cost and increase emissions out-of-state)
- CARB’s analysis found that under 2030 and 2045 scenarios, current output-based allocations effectively limit leakage for emissions-intensive, trade-exposed sectors, while border carbon adjustments, targeted electrification subsidies, and R&D support for low-carbon technologies could further reduce leakage and emissions from these industries.
CARB Public Input: With the adjusted allowance budgets, what level of industrial allocation is necessary to protect against emissions leakage? Given the loss of federal funding, should CARB use the Program to increase support for industrial decarbonization projects that reduce GHG emissions and protect against leakage in California? If so, what sectors and facility investments should be eligible for this support under Cap-and-Invest and through what approach?
Transition free allocations from gas to electric utilities to assist with growing electricity demand
- Background: Current regulation provides free allowances to both natural gas suppliers and electrical distribution utilities, to help shield consumers from higher energy prices. Certain utilities are required to consign their free allowances to auction (must sell CCAs and not hold for compliance obligation) The utilities then repurchase the allowances they actually need to cover their compliance obligation and the revenues from these allowance sales are returned to customers, primarily as the California Climate Credit that shows up as a bill rebate.
- AB1207 requires CARB has to phase out free allocations to natural gas utilities and redirect them to electric utilities by January 1, 2031. Electric utilities will receive more free allowances and thus more auction revenue to provide rebates, invest in electrification, or offset ratepayer costs as electricity demand grows
- CARB Public Input: Timing of the transition and how to treat different categories of utilities including Investor-Owned Utilities (IOUs), Publicly Owned Utilities (POUs), Electric Cooperatives and Federal Power Marketing Administrators.
What’s Next?
- Public comments are due by November 12, 2025
- Initial Statement of Reasons (ISOR) to be released by end of 2025
- The Board then votes on the final package likely by Q2 2026, with new regulation in effect by Sep 2026
- Linkage with Washington state Cap-and-Invest would require a subsequent rulemaking process and could be completed mid-2027
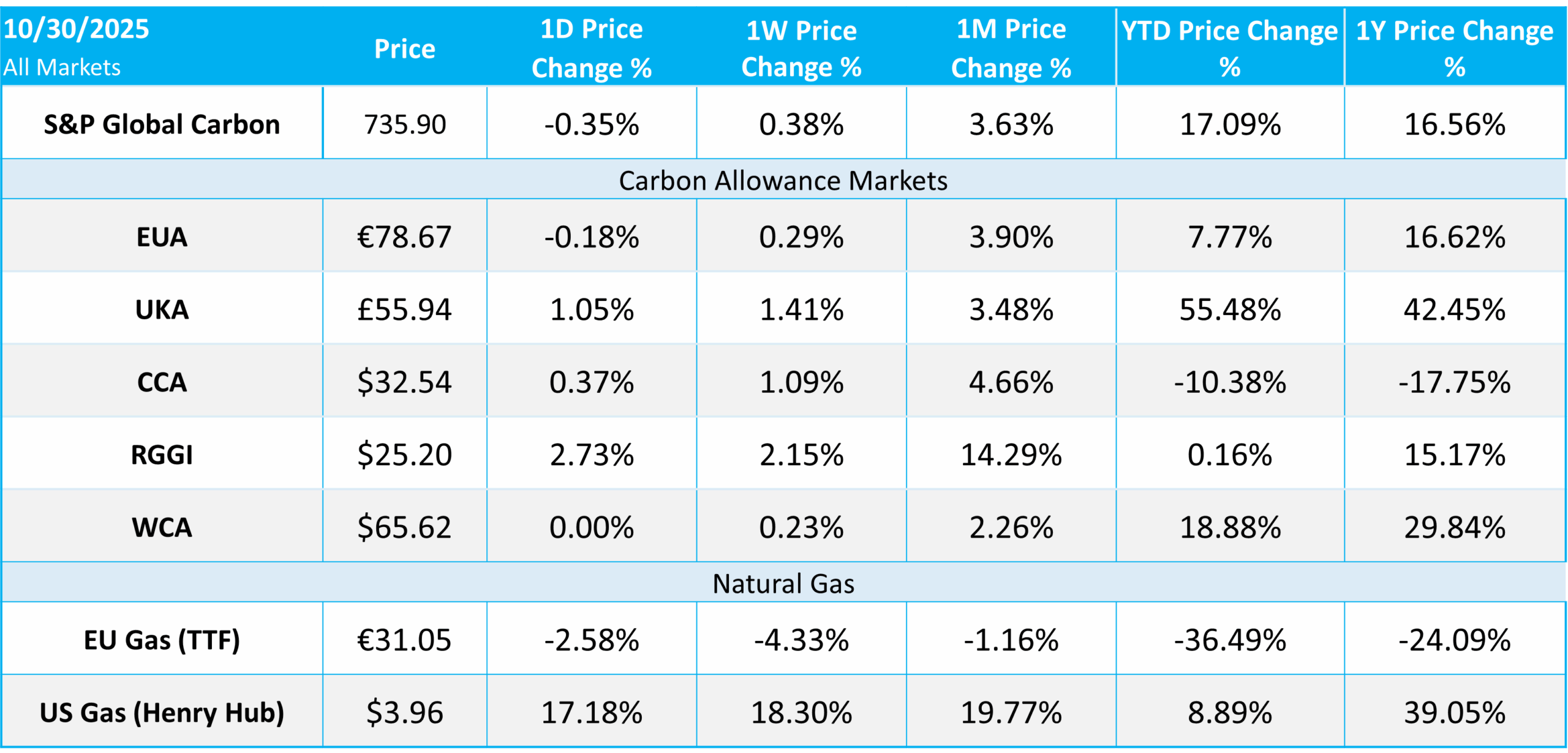
Carbon Market Roundup
The weighted global price of carbon was $55.43, up +0.24% week over week. EUAs were down -0.18% for the week at €78.67. UKAs were up +1.05% at £55.94. CCAs were up +0.37% for the week at $32.54. RGGI was up +2.73% at $25.20. WCAs were flat at $65.62.